Specialized Audiologists: What Areas Do They Focus On?
Entering the world of hearing health can seem complex if you’ve never

By: admin | December 21, 2020
Audiology is defined as a part of science that deals with balance, hearing and related disorders. It can be traced as far back as 1550 BC, when writings from the famous Ebers medical scroll revealed treatments for hearing loss.
Despite its ancient origins, not much progress had been made in audiology until the turn of the 19th and 20th centuries. Today audiology involves extremely advanced technology and is practiced by specialists known as audiologists. But what exactly does an audiologist do? You may be surprised to discover that their work goes far beyond just simple hearing issues. Want to know more? This is your guide to these audio experts and everything pertaining to their field.
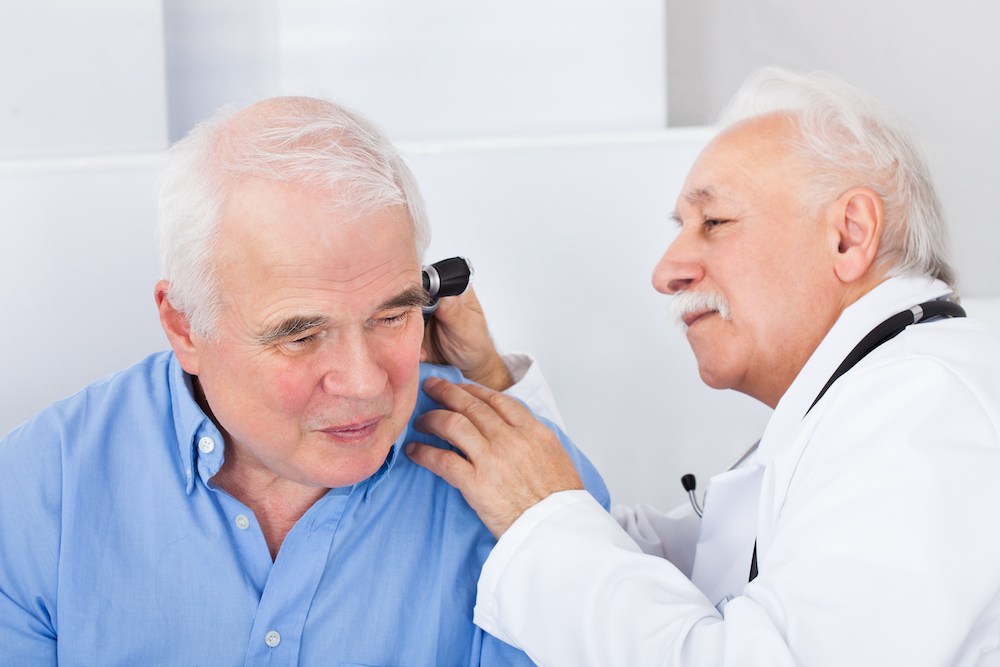
Audiologists are qualified healthcare professionals who handle issues related to the auditory system. Modern day audiologists use technology and creative reasoning to identify auditory disorders in people and help them communicate well when something isn’t how it should be. They are best known for diagnosing and prescribing treatments for hearing impairments.
As of 2019, the number of practicing audiologists in the United States was 13,590. However, experts predict that by 2028 there will be a 16% increase in practicing audiologists. Most of them work in healthcare facilities such as hospitals or audiology clinics. You can also find some in schools.
Audiologists perform a wide range of activities, including assessing, testing, diagnosing, and treating hearing disorders, tinnitus, and balance issues. They also play advisory roles by counseling patients on topics concerning their auditory health and treatment options. They are qualified to prescribe, fit, program, and manage hearing aids or cochlear implants. Pediatric Audiologists supervise many newborn hearing-screening tests.
Besides their primary task of treating hearing disorders, audiologists help with tinnitus and balance disorders like vertigo. The reason for this is that the human’s sense of balance originates from within the inner ear (called the cochlea). Therefore, audiologists help patients restore their balance through vestibular testing.
Audiologists that work within the field of Speech Pathology often work with children and adults to diagnose, assess, and treat speech or language related disabilities. Their tasks range from assisting people with speech and language problems, to helping people who experience problems when swallowing.
Many audiologists also conduct scientific research that contributes to knowledge in the field of audiology. These research studies help discover new ways of identifying, testing and diagnosing hearing and other related complaints.
Here are some of the main conditions that audiologists often work with:
Audiologists are required to have a Doctor of Audiology (AuD) postgraduate degree, which usually takes about four years to complete. After earning this degree, they must be licensed by the states in which they would like to practice, for which the process involves sitting an exam.
Many audiologists go on to achieve additional types of certifications which boost their credibility in the field. Some of these include the American Speech and Hearing Association (ASHA) and a Certificate of Clinical Competence (CCC). They can also acquire board certification from the American Academy of Audiology (AAA).
To summarize, auditory health is essential, and audiologists are here to help you keep it intact. But their vital work is not limited to just hearing disorders. It also includes the diagnosis and treatment of speech and communication problems to ensure that people experiencing hearing difficulties can continue to live full and happy lives.
Call this phone number to learn more about EarTech Audiology and what our audiologists can do for you: (866) 464-1008

Entering the world of hearing health can seem complex if you’ve never
By: admin | January 31, 2024

A pivotal figure in the workplace, a hearing specialist plays a crucial
By: admin | December 28, 2023
Hearing tests are essential for determining whether you have hearing loss
By: admin | November 25, 2023
